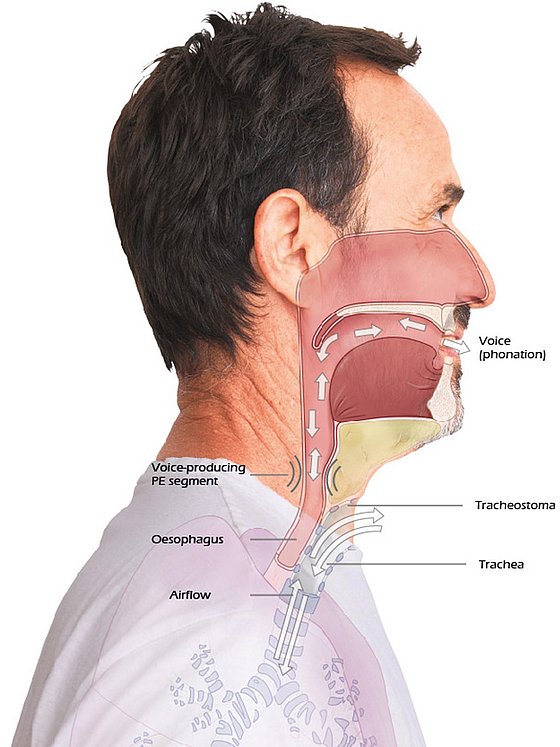
Ructus voice
In the ructus voice (oesophageal substitute voice), the air in the mouth is inhaled or pressed into the upper part of the oesophagus. This air remains there for a short period and is then transported back out of the oesophagus into the mouth in a controlled manner. This causes folds of mucous membrane at the upper edge of the oesophagus to vibrate.
This vibration creates a sound, which can then be articulated through movement of the mouth. The advantages of the ructus voice are that one has both hands free when speaking and does not need any additional aids. Regular speech therapy is highly recommended to learn this substitute voice.
Advantages of the ructus voice
- Individual voice character can be recognised
- Voice formation is possible without additional aids